What Are The Differences Between Plant And Animal Cells Quizlet
Cytokinesis Definition
Cytokinesis is a physical process of cell partitioning, that commonly takes place later mitosis. Cytokinesis is the concrete segmentation of the jail cell cytoplasm, the jail cell membrane, and cell organelles in eukaryotic cells to produce two distinct cells at the finish of the prison cell wheel in both mitosis and meiosis.
- In most cells, cytokinesis is initiated during the anaphase stage and ends in telophase, a phase where the chromosomes are completely segregated.
- In animal cells, cytokinesis is achieved when a contractile band of the jail cell microtubules form a cleavage furrow that divides the cell membrane into half. The microtubules used during cytokinesis are those generated during the initial stages of sectionalization and they contribute to the restructuring of the new cell.
- In the establish cell, a cell plate is formed that divides the cell into two.
- Additionally, cytokinesis simply takes place ones the separation of chromosomes is consummate. This ensures that each daughter cell receives a full fix of chromosomes forth with the complete elements of the cytoplasm and cell organelles.
What happens during cytokinesis?
- Cytokinesis is similar in both plant and fauna cells, however, it varies past the completion of the mechanism of the germination of two daughter cells from a parent cell, each with a set of separated chromosomes and halved cytoplasm and prison cell organelles.
- The division process of the cell by and large entails the formation of a cleavage furrow, which divided the cells almost equally.
- Cell division may be symmetrical or asymmetrical, where ane prison cell takes a majority of the cytoplasm.
- For example, spermatogenesis, a meiosis cell sectionalization process is symmetrical cytokinesis where the newly formed sperm cells are equal in size and content, while biogenesis is a typical example of asymmetrical cytokinesis, producing a large cell and iii polar bodies.
- The cleavage furrow in fauna cells is adamant by the positioning of the mitotic spindles while in institute cells, the cleavage furrow is contained of the mitotic spindles.
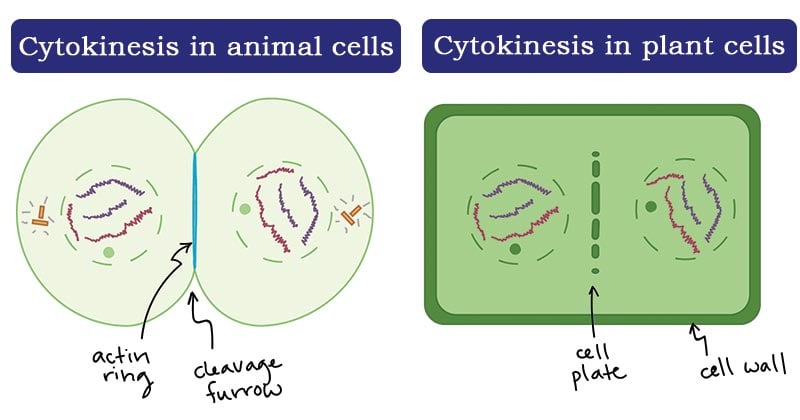
Figure: Cytokinesis in plant and animal cells. Image Source: Khan Academy.
Mostly, cytokinesis takes place in four stages:
Initiation and germination of the cleavage furrow
- During cytokinesis, the initial physical modify observed is the appearance of the cleavage furrow on the cell surface.
- The furrow starts to deepen, spreading effectually the cell until it completely divides into two.
Contraction and constriction
- This is also known as abscission.
- The accomplishment of cytokinesis in animal cells in past the contractile ring, which is a ring that is made up of actin and myosin and regulatory proteins formed under the surface of an animal cell during cell sectionalisation.
- These rings have the ability to contract and tuck the cell pinching it into two.
Membrane Insertion
- Concurrently, a new membrane is formed and inserted into the cell membrane, side by side to the contractile ring through the fusion of the intracellular vesicles.
- The new membrane enables the jail cell to increase as the cytoplasmic segmentation takes place.
Completion of cytokinesis past forming two fully adult daughter cells.
Cytokinesis in beast cells
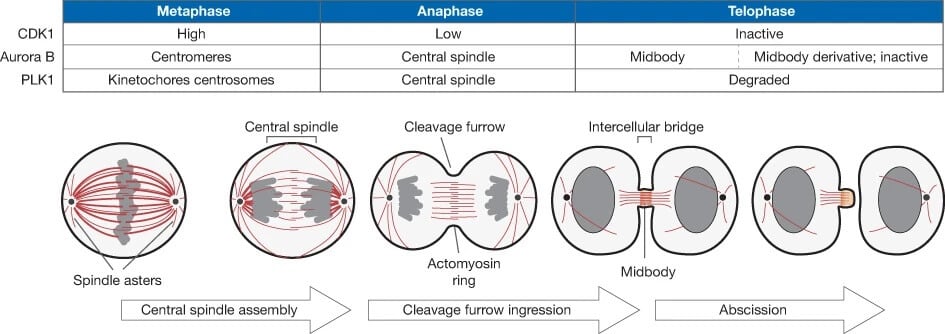
Effigy: A schematic representation showing the reorganization of an fauna prison cell progressing through the different stages of cytokinesis. Cerise, microtubules; grey, chromosomes. Image Source: Nature Prison cell Biology.
- The cytokinesis process in the creature cell is attributed to the role of the contractile ring. The contractile ring is held together past the microtubules of the mitotic spindles.
- These microtubules and cell signals determine the location of the contractile ring and therefore they direct the plane of cell division, known every bit the partition aeroplane.
- The cleavage furrow forms around the division plane which somewhen pinches off separating the cell into 2 cells.
- This is followed by a procedure of wrinkle and constriction past the contractile ring, fabricated upwards of actin, myosin, and regulatory proteins.
- Actin and myosin are formed during interphase assembled in a cortical network o the filaments filled with actin and myosin. Every bit prison cell division continues, actin filaments are reorganized while the myosin filaments accumulate during anaphase to form the contractile rings.
- The contractile ring is positioned by the actin-myosin and regulatory proteins and they also act every bit the motor proteins, allowing the contraction of the muscle cells.
- The musculus cells which are packed with actin filaments are pulled together by myosin proteins to grade an actin-myosin ring, which plays a major role in the exclusion of the cytoplasm and the cell organelles.
- After the exclusion of the cytoplasm and the organelles, the ring and the microtubules are left behind forming the midbody structure, which eventually divides.
- The cellular proteins cut and fusion of the plasma membrane are shut, while the extracellular elements that hold the cell together become dissolved, separating the cells.
- The separated cells may remain associated linked by the cytoplasm at bridges known as the gap junctions, which are formed past remains of the endoplasmic reticulum trapped past the midbody structures.
Cytokinesis in plant cells
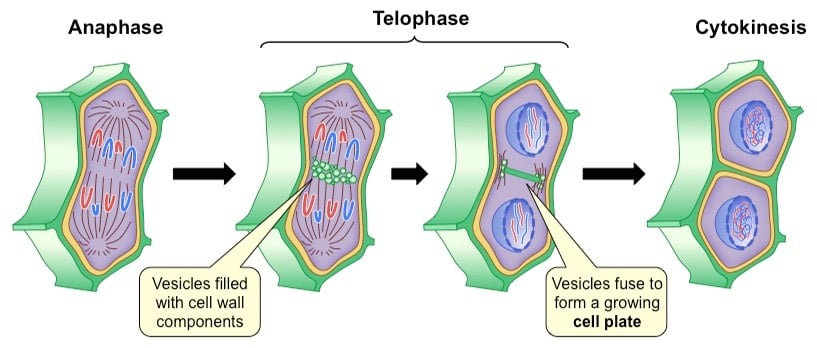
Figure: Cytokinesis in institute cells. Paradigm Source: BioNinja.
- The major difference between an brute cell and a institute cell is that plants are made up of an extra-rigid prison cell wall, and therefore, a special kind of microtubules are involved in the completion of cytokinesis. These are known as the phragmoplasts.
- Phragmoplasts are vesicular spindle microtubules formed past Golgi vesicles during telophase on the metaphase plate, carrying vesicles and cellular elements such equally cellulose to the new cell wall.
- When these Golgi vesicles fuse at the center next to the cell wall, they grade the cell plate, the site of establish cytokinesis.
- The more the vesicles fuse, the cell plate continues to enlarge, emerging at the periphery of the prison cell wall of the cell.
- The phragmoplasts carry vesicles of the cell wall to the newly formed cell plate.
- Accumulated enzymes, structural proteins, and glucose molecules between the membranes by the Golgi appliance during interphase contribute to the formation of the new prison cell wall, while the Golgi membranes are incorporated and form part of the plasma membrane.
- The cellulose carried by the phragmoplast interact and combine forming the complex and potent rigid matrix of the plant cell wall.
- Later the cell plate divides the cell, the plasma membrane seals off separating the two newly formed daughter cells.
- In between the two cells, trapped endoplasmic reticulum forms the plasmodesmata, space, or gap which allows the passage of molecules from one cell to another and signaling of cells for cell communication.
Applications of Cytokinesis
- Cytokinesis studies have enabled the construction of block-cytokinesis micronuclei cytosome assay to written report man lymphocytes.
- Failed cytokinesis can pb to tumorigenesis which has enhanced cancer studies in the agreement of oncogenesis and drug targets to unfulfilled cytokinesis processes.
References and Sources
- i% – https://www.thoughtco.com/cytokinesis-in-a-cell-cycle-373541
- 1% – https://www.researchgate.cyberspace/publication/226631723_Molecular_Analysis_of_the_Cell_Plate_Forming_Machinery
- ane% – https://world wide web.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2789570/
- 1% – https://quizlet.com/200759728/bio-121-chapter-12-flash-cards/
- i% – https://courses.lumenlearning.com/dizzying-biology/affiliate/the-cell-bicycle/
- <i% – https://www.thoughtco.com/daughter-cells-defined-4024745
- <i% – https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/cytokinesis
- <1% – https://www.majordifferences.com/2013/10/difference-plant-jail cell-vs-and-beast-jail cell.html
- <1% – https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Plasma-Membrane
- <ane% – https://www.cell.com/electric current-biology/pdf/S0960-9822(11)01205-X.pdf
- <1% – https://world wide web.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/x.1146/annurev.cellbio.17.1.351
- <ane% – https://study.com/academy/lesson/actin-filaments-function-structure-quiz.html
- <1% – https://quizlet.com/11000697/molecular-biology-of-the-cell-chapter-17-part-three-wink-cards/
- <one% – http://absuriani.my/Book%20CHAPTER/2018%20chapter%201.pdf
Source: https://microbenotes.com/cytokinesis/
Posted by: avalostimperall.blogspot.com

0 Response to "What Are The Differences Between Plant And Animal Cells Quizlet"
Post a Comment